Intro: The phrase No Kings has become a powerful motif in college football, symbolizing the unpredictable nature of the sport and the potential for any team to rise above the rest. As the 2023 season unfolds, the LSU vs Vanderbilt matchup and the Washington vs Michigan clash are set to captivate fans with their blend of tradition, strategy, and emerging talent. These games represent more than just a weekend of football; they are pivotal moments that could redefine the trajectory of these programs. Whether it's the LSU Tigers’ dominance on the field meeting Vanderbilt Commodores’ resilience, or the Washington Huskies’ innovative playstyle clashing with Michigan Wolverines’ storied legacy, both contests promise to deliver high-stakes drama. This article delves into the historical context, current dynamics, and tactical insights of these matchups, offering a comprehensive analysis of why they matter for the No Kings era. — Section 1: The Historical Context of LSU vs Vanderbilt The rivalry between the LSU Tigers and Vanderbilt Commodores is rooted in the early days of college football, dating back to 1893. Though it’s not as intense as the SEC’s traditional powerhouses, the LSU vs Vanderbilt matchups have always carried weight, especially when the stakes are high. Over the years, these games have highlighted the contrast between LSU’s reputation as a powerhouse and Vanderbilt’s underdog status. While LSU has often dominated, the Commodores have consistently shown grit and tactical ingenuity, keeping the rivalry competitive. 1.1 Origins of the Rivalry The first meeting between LSU and Vanderbilt occurred during the 1893 season, a time when the sport was still in its formative stages. The rivalry, however, gained more traction in the early 20th century, particularly in the 1920s and 1930s, when LSU was rising as a national powerhouse and Vanderbilt was carving out its identity in the South. Despite the gap in prestige, the LSU vs Vanderbilt games have always been marked by a blend of passion and strategic depth, with each team bringing its unique style to the field. 1.2 Past Meetings and Key Moments Historically, LSU has held the upper hand in their matchups, with a record of 23 wins and 15 losses against Vanderbilt as of 2023. Notable moments include LSU’s 1993 upset victory, which saw the Tigers overcome a 14-7 deficit in the final minutes to secure a 21-17 win. This game remains a testament to LSU’s resilience. Conversely, Vanderbilt has had moments of brilliance, such as their 2017 win over a ranked LSU team, which showcased their ability to challenge even the most established programs. 1.3 Current Standing and Psychological Edge As the 2023 season progresses, the LSU vs Vanderbilt matchup is expected to be a critical test for both teams. LSU, led by head coach Brian Kelly, has entered the season with high expectations, boasting a strong defense and a balanced offense. Meanwhile, Vanderbilt aims to build on their recent improvements, with a renewed focus on discipline and execution. The psychological edge in these games often hinges on momentum—whether it’s a late-game heroics or a defensive stop that can shift the narrative. — Section 2: The Legacy of the Washington vs Michigan Rivalry The Washington vs Michigan rivalry is one of the most storied in college football, with a history that spans over a century. Known as the “Big Game,” this matchup has produced unforgettable moments, from dramatic comebacks to historic upsets. The Washington Huskies and Michigan Wolverines have faced each other 45 times, with Michigan holding a slight edge in the series (21-18-6). However, the No Kings era has made these games even more unpredictable, as both programs have shown the ability to rise or fall in a single week. 2.1 Historical Significance and Milestones The rivalry between Washington and Michigan dates back to 1890, making it one of the oldest in the nation. The two teams first met in 1890 when Washington lost 22-0 to Michigan, a game that set the tone for future matchups. Over the decades, the series has been a barometer of success, with Michigan often regarded as a perennial powerhouse. However, Washington has clawed its way back into contention, especially in the 2000s and 2010s, with key victories that showcased their growing competitiveness. 2.2 Key Moments and Iconic Games Some of the most iconic games in the Washington vs Michigan series include Michigan’s 2006 win over Washington in the Rose Bowl, which sealed their national championship. More recently, Washington’s 2019 upset victory in Ann Arbor, where the Huskies edged out the Wolverines 23-20, became a turning point in the rivalry. These moments highlight the emotional and strategic depth of the series, where underdog triumphs and dominant performances coexist. 2.3 Modern Dynamics and Competitive Balance In the 2023 season, the Washington vs Michigan matchup is poised to be a clash of styles. Washington has embraced a modern, spread offense under coach Jimmy Lake, while Michigan continues to rely on its signature physicality and defensive strength. The series now reflects a broader trend in college football, where parity is the norm and the underdog can disrupt the traditional hierarchy. This dynamic makes the No Kings phrase particularly relevant, as neither team can be guaranteed an easy path to victory. — Section 3: Tactical Strategies and Game Plan for LSU vs Vanderbilt The LSU vs Vanderbilt game is a test of both preparation and adaptability. LSU, known for its high-powered offense and defensive expertise, faces the challenge of outsmarting a Vanderbilt team that has shown an ability to execute under pressure. The key to success in this matchup lies in understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each squad, as well as the strategic decisions that can tip the scales in a crucial contest. 3.1 LSU’s Offense and Defensive Strategy LSU’s offense, led by quarterback Myles Brennan, has been a focal point of the team’s success. The Tigers’ wide receiver corps, featuring Ja’Marr Chase and Terrace Thomas, poses a significant threat in the passing game. Defensively, LSU has relied on its aggressive scheme, with a strong secondary and a
How to Secure Your Home WiFi Network: Tips for Safety
How to Secure Your Home WiFi Network: Tips for Safety In today’s digital age, securing your home WiFi network is more critical than ever. With the rise of cyber threats and the increasing number of connected devices in households, a how to secure your home WiFi network strategy is essential to protect your personal data, privacy, and even your smart home ecosystem. A weak WiFi network can leave your home vulnerable to hackers, data breaches, and unauthorized access. This article will guide you through the most effective how to secure your home WiFi network methods, from changing default settings to enabling advanced security features. Whether you're a tech novice or an experienced user, these steps will help you create a safer, more reliable network environment for your family and devices. — 1. Understanding WiFi Security Vulnerabilities Before diving into securing your WiFi network, it’s crucial to recognize the common vulnerabilities that make your network susceptible to attacks. One of the biggest risks comes from default settings used by most routers. Manufacturers often set generic usernames and passwords, which are easy for hackers to exploit. For example, many routers use "admin" as the default login and "password" as the default password. These are simple to guess, leaving your network exposed. Another major threat is unencrypted data transmission. If your WiFi network doesn’t use encryption, anyone within range can intercept your internet traffic, including sensitive information like login credentials, credit card details, and personal messages. This is why WPA3 encryption (or WPA2, if WPA3 isn’t supported) is a must. Without it, your network becomes a target for eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks. Additionally, outdated firmware can introduce security loopholes. Routers and devices are constantly updated to patch vulnerabilities and improve performance. If you don’t keep your firmware current, you’re leaving your network open to known exploits. A 2023 report by the Ponemon Institute found that 62% of cyberattacks on home networks exploit outdated firmware. Understanding these risks sets the foundation for implementing robust security measures. — 2. Changing Default Settings for Enhanced Security Default settings are the first line of defense against unauthorized access. Most routers come with preconfigured usernames and passwords, which are often easy to crack. The first step in securing your home WiFi network is to change these defaults. 1. Modify the SSID (Network Name) The Service Set Identifier (SSID) is the name of your WiFi network. By default, it might be something like "TP-Link1234&quot;</strong> or <strong>&quot;Netgear2023", which reveals information about your router brand and model. Hackers can use this data to target specific vulnerabilities. Rename your SSID to something unique and personal, such as "MyHomeNetwork" or "SecureWiFi_2024", to make it harder for intruders to identify your router. 2. Update Default Passwords Replace the default password with a strong, unique one. Use a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Avoid using passwords like "12345678" or "password". A 2022 study by the UK’s National Cyber Security Centre showed that 70% of WiFi breaches involved weak or reused passwords. Consider using a password manager to generate and store complex passwords securely. 3. Change Admin Credentials Your router’s admin login is a key entry point for attackers. Change the default admin username and password to something more secure. For example, instead of "admin", use "RouterAdmin2024", and set a strong password. This prevents unauthorized users from accessing your router’s settings and making changes without your consent. — 3. Using Strong Passwords and Encryption A strong password is one of the simplest yet most effective ways to secure your home WiFi network. Pairing it with the right encryption protocol ensures that your data is protected from prying eyes. 1. Create a Complex Password Your WiFi password should be at least 12 characters long and include a mix of letters, numbers, and symbols. Avoid using predictable patterns or personal information like birthdays. For example, instead of "Summer2023!", use "s@7!GwQ9zL$2". A 2023 survey by the Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) found that 65% of users still rely on weak passwords, making them easy targets for brute-force attacks. 2. Enable WPA3 or WPA2 Encryption Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) encryption is crucial for securing your network. WPA3 is the latest standard, offering stronger security than its predecessor, WPA2. If your router doesn’t support WPA3, use WPA2. Ensure that WPA3/WPA2 is enabled in your router’s settings, and avoid using WEP encryption, which is outdated and easily crackable. 3. Use a Separate Password for Public Networks When connecting to public WiFi, always use a different password than your home network. Public networks are often less secure, and a weak password could allow hackers to access your personal data. For instance, WiFi networks in cafes or airports are frequently targeted by cybercriminals. Even if your home network is secure, a weak public password can compromise your account if you log in to it. — 4. Monitoring and Managing WiFi Activity Once your network is secured, the next step is to monitor and manage its activity. This helps you identify suspicious behavior and ensure that only authorized devices are connected. 1. Check Connected Devices Regularly Log in to your router’s admin panel to review the list of devices connected to your network. If you see unfamiliar devices, investigate further. For example, if you notice a device like "IoTDevice123" or "Printer_2023", it could be a rogue device connected without your knowledge. Regularly auditing devices helps detect unauthorized access or data leaks. 2. Use Parental Controls and Bandwidth Management Parental controls can restrict access to certain websites or limit usage for specific devices, especially if you have children. Bandwidth management ensures that no single device consumes excessive data, which can slow down your network or indicate a security threat. For instance, a device using 10GB of data in a single hour might be streaming pirated content or downloading malware. 3. Set Up a Guest Network Create a separate guest WiFi network for visitors to use. This isolates their devices from your main network, reducing the risk of them accessing
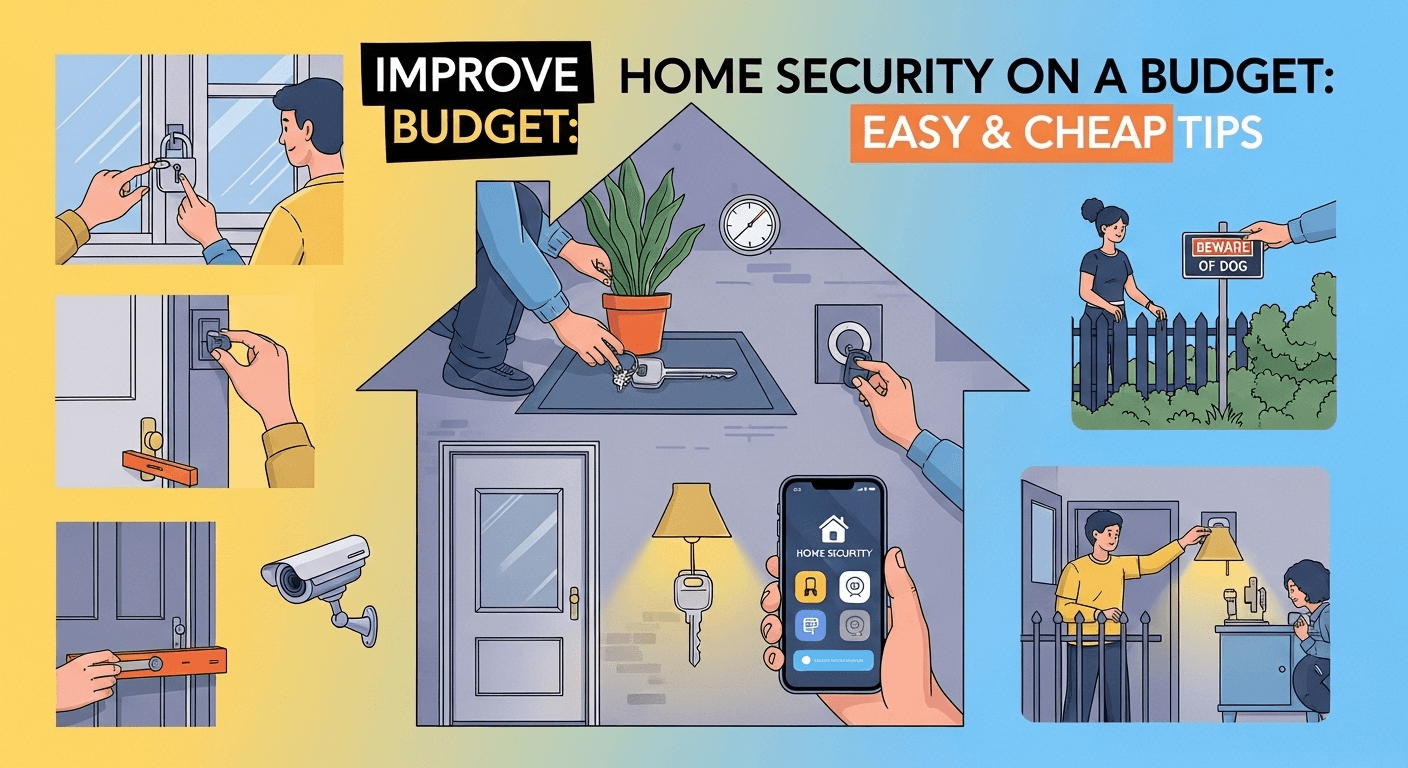
Improve Home Security on a Budget: Easy & Cheap Tips
Feeling secure in your own home is a fundamental need, not a luxury. However, the high price tags on advanced security systems and professional services can make robust protection feel out of reach for many. The good news is that you don't need to break the bank to significantly bolster your home's defenses. There are numerous effective, affordable, and often simple strategies you can implement right away. This guide is designed to walk you through exactly how to improve home security on a budget, proving that a safe and secure home is achievable for everyone, regardless of their financial situation. We'll explore a layered approach, from fortifying your physical barriers to leveraging low-cost technology and the power of community. Improve Home Security on a Budget: Easy & Cheap Tips Fortify Your First Line of Defense: Doors and Windows The vast majority of burglars gain entry through a door or a first-floor window. These are the most common and predictable points of vulnerability in any home. Therefore, making them as difficult as possible to breach is the single most effective and cost-efficient security measure you can take. A would-be intruder is looking for a quick and quiet entry; by adding just a few layers of resistance, you can convince them to move on to an easier target. This foundational step doesn't require expensive technology, but rather a focus on strengthening the physical integrity of your home's entry points. Strengthening these areas is all about creating delays and obstacles. Think like a burglar: what would be the easiest way in? Is it the flimsy lock on the back door? The old window in the guest room that doesn't latch properly? By identifying and addressing these weak spots with simple, inexpensive hardware upgrades, you are making a massive improvement. This proactive approach transforms your home from a soft target into a hardened one, a concept that is central to residential security. The goal is to make the effort and noise required to break in not worth the potential reward. Many of the most impactful upgrades in this category can be done as a DIY project with basic tools, saving you the cost of professional installation. Hardware stores are treasure troves of affordable security solutions, from stronger screws to more robust locks and window films. Investing a small amount of money and a bit of your time here will yield the highest return on investment for your home's overall security posture. It's the logical and most crucial starting point for anyone serious about security on a budget. Reinforce Your Doors Your primary entry doors—front, back, and garage-to-home—are critical checkpoints. A standard lockset installed by a builder might look secure, but it often has a critical weakness: short screws that only grip the soft wood of the doorjamb. The first and cheapest upgrade is to replace these short screws in your lock’s strike plate with 3-inch coated deck screws. These longer screws will anchor the strike plate deep into the solid wood of the wall stud behind the jamb, making the door frame vastly more resistant to being kicked in. This is a five-dollar fix that can stop a brute-force entry attempt cold. Next, ensure every exterior door has a quality deadbolt lock. If you only have a locking doorknob, you are highly vulnerable. A Grade 1 or Grade 2 deadbolt provides a significant security boost. Look for one with a one-inch throw (the length the bolt extends into the frame). For an extra layer of protection, especially at night or when you're home, consider a door security bar or a door jammer. These portable devices brace against the floor and prevent the door from being opened, even if the lock is bypassed. They are inexpensive, require no installation, and are perfect for renters. Secure Your Windows Windows are another favorite entry point for burglars, especially those on the ground floor or hidden from street view. The factory latches on many windows are flimsy and can be easily forced open. A simple and cheap upgrade is to install secondary window locks or keyed locks. These can be purchased for just a few dollars each and prevent the window from being slid or lifted open. For an even simpler DIY solution, you can drill a hole through the window sash and into the frame and insert a strong nail or pin, which physically blocks the window from opening. Another excellent, albeit slightly more expensive, option is to apply a security window film. This transparent polyester film adheres to the inside of your glass. While it won't make the glass unbreakable, it holds the shattered pieces together if a burglar tries to smash it. This creates a significant delay and a lot of noise, two things an intruder wants to avoid. It also offers the side benefits of UV protection and privacy. For ground-floor windows, especially those in the back of the house, this film can be a game-changer in your budget security plan. The Power of Perception: Making Your Home an Unattractive Target A significant part of home security is psychological warfare. Burglars are fundamentally opportunists who operate on a risk-versus-reward calculation. They actively seek out homes that appear unoccupied, unmonitored, and easy to access. Your goal is to disrupt this calculation by making your home look like a "hard target"—a place where the risk of being seen, caught, or delayed is simply too high. This is where deterrence comes into play, and you can achieve powerful deterrent effects with minimal spending. This strategy is all about creating an environment of perceived risk for the potential intruder. It involves sending clear signals that your home is occupied and protected, even when it isn't. Small visual cues can have an outsized impact on a burglar's decision-making process. A well-lit porch, a car in the driveway, and the absence of piled-up mail all suggest that someone is home and alert. These are simple, common-sense practices that cost nothing but contribute significantly to your overall security. By consistently
Top Signs Your Computer Has Been Compromised by Malware
In an era where our lives are deeply intertwined with our digital devices, the health of our computers is paramount. A machine running smoothly is a gateway to productivity, entertainment, and connection. However, when it starts to act erratically, it can be a source of immense frustration and anxiety. The culprit is often malicious software, or malware, working silently in the background to steal your data, disrupt your activities, or use your machine for nefarious purposes. Recognizing the problem is the first and most critical step toward a solution. It's crucial to recognize the common signs your computer has been compromised by malware to act quickly, mitigate the damage, and reclaim your digital security. This guide will walk you through the top indicators that your machine has been infected. 1. Severe Performance Degradation: The Most Obvious Clue One of the most immediate and noticeable signs of a malware infection is a sudden and drastic decline in your computer's performance. If your once-zippy machine now takes ages to boot up, struggles to open applications that used to launch instantly, or freezes frequently for no apparent reason, malware could be the hidden cause. This isn't about the gradual slowing that happens over years of use; this is a marked drop in speed that seems to have come out of nowhere. Malicious programs are often poorly coded and run aggressive processes that consume a significant amount of your system's resources, such as CPU power and RAM. This resource drain is what causes the sluggishness. Malware can be running intensive calculations for crypto-mining, scanning your files for sensitive data, or replicating itself in the background—all of which put an immense strain on your hardware. You might also experience frequent system crashes, including the infamous "Blue Screen of Death" (BSOD) on Windows. While crashes can have many causes, malware that interferes with critical system files or drivers can easily lead to this kind of instability. If your computer has become unreliable and frustratingly slow, it's time to investigate for a potential infection. Furthermore, a slow internet connection on a specific device can also be a red flag. If your internet is fast on your phone and other devices but crawls to a halt on your primary computer, malware might be hijacking your bandwidth. It could be using your connection to send out spam emails, participate in a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack as part of a botnet, or upload your stolen data to a remote server. This constant, unauthorized network activity monopolizes your internet connection, leaving very little for your legitimate browsing, streaming, or gaming needs. 1. Unexplained Resource Hogging To get concrete evidence of a resource hog, you can use your system's built-in monitoring tools. On Windows, this is the Task Manager (accessible by pressing Ctrl+Shift+Esc), and on macOS, it's the Activity Monitor (found in the Utilities folder). Navigate to the "Processes" or "CPU" tab and look for any programs or processes that are consistently using a very high percentage of your CPU, memory (RAM), or disk. Pay close attention to processes with strange, nonsensical names (e.g., "svc.exe," "run32.dll.exe") or those that lack a clear description. While it's normal for demanding applications like video editors or games to use a lot of resources while you're using them, it is highly suspicious if an unknown process is consuming 99% of your CPU when your computer is supposed to be idle. Malware often tries to disguise itself with names similar to legitimate system files to avoid detection. If you find such a process, a quick internet search of the process name can often reveal whether it is a known malicious entity. Do not terminate a process unless you are sure it is malicious, as ending a critical system process can cause your computer to crash. 2. The Mystery of Vanishing Disk Space Another perplexing sign of a malware infection is the unexplained loss of hard drive space. You check your storage and find that gigabytes have vanished, even though you haven't installed any large programs or downloaded massive files. This can happen for several reasons, all tied to malware. Some types of viruses are designed to replicate themselves rapidly, filling your drive with copies until there's no space left. This can slow your system to a crawl and prevent you from saving new files. Other forms of malware may download additional malicious payloads, tools, or stolen data onto your drive without your knowledge. A piece of spyware, for instance, might be recording your screen or logging your keystrokes and saving these large files locally before attempting to upload them. While it's important to first rule out legitimate causes—such as system restore points, Windows update files, or a browser cache that needs clearing—a sudden and significant drop in free space that you cannot account for is a strong indicator of malware activity. 2. Annoying Intrusions: Pop-ups, Toolbars, and Homepage Changes If your browsing experience has turned into a nightmare of constant interruptions, adware is likely to blame. Adware is a type of malware specifically designed to bombard you with advertisements. This goes far beyond the normal ads you see on websites. We're talking about pop-up windows that appear even when your browser is closed, ads that cover the content you're trying to read, and banners for suspicious products appearing on sites where they don't belong. These intrusions are not just annoying; they are a serious security risk. These pop-ups often promote scams, fake software ("Your PC is infected! Download our cleaner now!"), or link to websites that can install even more dangerous malware, such as spyware or ransomware. Clicking on anything—even the "X" to close the window—can sometimes trigger a malicious download. This type of aggressive advertising is a clear signal that a program has been installed on your computer without your full consent and is now controlling parts of your online experience for financial gain. The problem is often compounded by browser hijacking. A browser hijacker is a specific type of malware that changes
Alabama vs. Missouri: Key Matchups for the Big Game
The world of college football is a vibrant tapestry of fierce rivalries, tactical battles, and national championship dreams. Each week brings matchups that can define a season, and the upcoming Alabama vs. Missouri contest is no exception, promising a clash of styles and ambitions that has fans buzzing. While other significant games, such as the Big Ten showdown between Ohio state vs illinois, also command attention for their own conference implications, the SEC battle holds a unique weight. As the digital age connects disparate topics, it’s a curious reality that search queries can lead viewers from a wide array of interests—whether you're a die-hard football fan, or even if your search for updates on figures like ian watkins has unexpectedly brought you here—to the heart of the gridiron action. This deep dive will focus squarely on the critical factors that will decide the Alabama versus Missouri game, a contest poised to be a season-defining moment for both programs. The Stakes: More Than Just Another SEC Game Every game in the Southeastern Conference (SEC) carries immense weight, but when a perennial powerhouse like Alabama meets a surging challenger like Missouri, the implications ripple across the national landscape. This isn't merely a game for conference standing; it's a litmus test. For Alabama, it's about maintaining their dynasty, reinforcing their claim as the team to beat, and keeping their path to the College Football Playoff clear. For Missouri, it represents a golden opportunity to score a signature win, to prove they belong in the conversation with the SEC's elite, and to potentially throw the entire conference race into chaos. A victory for the Tigers would be a program-defining moment, while a loss could be a minor bump or a-season-derailing disaster for the Crimson Tide. The pressure on Alabama is a constant, a self-imposed standard of excellence. Anything less than a national championship is often viewed as a disappointment. This game falls into a critical part of their schedule where momentum is paramount. The coaching staff and players operate under the microscope of national media and a demanding fanbase. Every play call, every missed tackle, and every penalty is scrutinized. Their goal is not just to win, but to dominate in a way that sends a clear message to future opponents and the playoff selection committee. This relentless pursuit of perfection is what fuels the Alabama machine, making every regular-season game a must-win scenario. Conversely, Missouri enters this contest with a different kind of pressure—the pressure of opportunity. The Tigers have steadily built a competitive roster and a resilient team culture. They are no longer a team that is simply happy to compete; they expect to win. A matchup against Alabama is the ultimate measuring stick. It’s a chance to validate their progress and announce their arrival on the national stage. An upset victory would not only be a monumental boost for recruiting but would also reshape the narrative around the program, transforming them from a tough out into a legitimate conference contender. The energy in their locker room will be electric, fueled by the desire to shock the college football world. Offensive Clash: Alabama's Power vs. Missouri's Precision When these two teams take the field, fans will witness a fascinating contrast in offensive philosophies. Alabama has historically been known for its physical, pro-style offense that aims to control the line of scrimmage and wear down opponents with a powerful running game. This sets up explosive play-action passes downfield to their roster of elite, NFL-caliber wide receivers. Their offense is built on overwhelming opponents with superior talent and punishing physicality, forcing defenses to break over the course of four quarters. It's a methodical and brutal approach that has proven incredibly effective for over a decade. Missouri, on the other hand, often relies more on a rhythm-and-precision-based attack. Their offense is designed to get the ball out of the quarterback's hands quickly, utilizing spread concepts to create favorable one-on-one matchups in space. They focus on high-percentage throws, quarterback efficiency, and allowing their skilled receivers to make plays after the catch. While they can certainly run the ball, their identity is often tied to a smart, well-executed passing game that can nickel-and-dime a defense down the field or strike quickly when a weakness is exposed. This chess match between Alabama's brute force and Missouri's sharp execution will be a central theme of the game. The success of each offense hinges on its ability to impose its will on the opposing defense. For Alabama, the key will be establishing their ground game early. A successful rushing attack opens up the entire playbook, holding linebackers and safeties in check and creating opportunities for deep shots. If Missouri's front seven can slow down the Tide's running backs, it will force Alabama into more predictable passing situations. For Missouri, the challenge is to protect their quarterback and give him the time needed to dissect the Alabama secondary. Quick passes, screen plays, and a disciplined approach will be crucial to neutralizing the Tide's ferocious pass rush and sustaining drives. 1. Quarterback Duel: The Field Generals At the heart of this offensive battle is the quarterback position. Alabama's quarterback is the conductor of a high-powered orchestra, tasked with managing the game, making smart decisions, and delivering the ball to a wealth of dynamic playmakers. Often a dual-threat, the Tide's signal-caller must possess not only a strong arm but also the athleticism to extend plays with his legs. His ability to remain poised under pressure, especially on crucial third downs and in the red zone, is what separates a good performance from a game-winning one. His decision-making against a disciplined Missouri defense—knowing when to force a throw and when to check it down or run—will be a critical factor in the game's outcome. Missouri's quarterback, in contrast, is the epitome of efficiency and a master of the offensive scheme. He thrives on accuracy, timing, and pre-snap reads. His primary job is to distribute the ball to the right player at the right
How to Create a Strong Password to Protect Your Accounts
In an era where our lives are increasingly intertwined with the digital world, the security of our online accounts has never been more critical. From banking and email to social media and work-from-home portals, a single compromised account can lead to a cascade of disastrous consequences, including financial loss, identity theft, and reputational damage. The first and most fundamental line of defense against these threats is a robust, well-crafted password. Many people underestimate this simple security measure, opting for convenience over protection, making them easy targets for cybercriminals. This guide will provide you with everything you need to know about how to create a strong password, moving beyond outdated advice to give you modern, practical strategies to secure your digital life effectively. The Anatomy of a Weak Password (And Why You're a Target) Understanding what makes a password weak is the first step toward creating a strong one. Weak passwords are the low-hanging fruit for hackers, and they are far more common than you might think. Typically, they fall into predictable categories: common words like password or 123456, personal information such as your name, your pet's name, or your birthdate, and simple keyboard patterns like qwerty or asdfghjkl. These are the first things an attacker will try, either manually or through automated software, because they have a high success rate against the average user. The psychology behind choosing weak passwords is understandable. We are creatures of habit and convenience. The human brain is wired to remember simple patterns and meaningful information, not long strings of random characters. This is why we default to using our child's birthday or the name of our favorite sports team. The problem is that this information is often publicly available or easily guessable, especially with the amount of data we share on social media. Hackers exploit this human tendency relentlessly through methods like brute-force attacks (trying every possible combination), dictionary attacks (using lists of common words and phrases), and credential stuffing (using leaked passwords from one site to try and log into others). Your "insignificant" accounts are just as valuable to hackers as your primary ones. An attacker might not care about your old forum account, but if you've reused that same weak password for your email, they have just hit the jackpot. Your email is often the key to your entire digital kingdom, allowing them to reset passwords for your bank, social media, and other critical services. This domino effect is why every single account, no matter how trivial it seems, needs a unique and strong password. You are a target not necessarily because of who you are, but because your data has value, and a weak password is an open invitation. Core Principles of Creating an Unbreakable Password To effectively learn how to create a strong password, you must internalize three core principles: length, complexity, and uniqueness. These three pillars work together to build a formidable barrier against unauthorized access. If your password is weak in any one of these areas, its overall security is significantly compromised. Think of it as a three-legged stool; remove one leg, and the entire structure collapses. Modern hacking tools can test billions of combinations per second, rendering short, simple passwords almost instantly crackable. Length is Your Greatest Ally When it comes to password strength, length is exponentially more important than complexity. Every additional character you add to your password increases the number of possible combinations dramatically, making it exponentially harder for a brute-force attack to succeed. A simple 8-character password using only lowercase letters has billions of combinations, but a modern computer can crack it in a matter of hours or days. A 16-character password using the same character set would take centuries. Outdated advice often focused on an 8-character minimum, but this is no longer sufficient. Today, security experts recommend a minimum of 12 to 16 characters for your most important accounts. For your master password on a password manager, a length of 20 characters or more is an excellent goal. The longer your password, the more time and computational resources an attacker would need to crack it, making you a much less appealing target. They will simply move on to someone with a weaker, shorter password. Complexity Adds Another Layer of Defense Complexity refers to the variety of character types you use. A strong password should be a mix of: Uppercase letters (A-Z) Lowercase letters (a-z) Numbers (0-9) Symbols (!, @, #, $, %, ^, &,, etc.) Adding complexity thwarts dictionary attacks. A hacker’s software might be programmed to try every word in the English dictionary, but it's much harder when that word is modified with numbers, symbols, and varied capitalization (e.g., `house` vs. `H0use!`). However, relying on simple, predictable substitutions (like replacing 'o' with '0' or 'a' with '@') is a well-known trick that modern cracking dictionaries account for. Therefore, complexity should be used to enhance a long password, not to make a short password feel secure. A password like `P@ssw0rd1` is still weak because its root is a common word. Uniqueness is Non-Negotiable This is perhaps the most critical and often-overlooked principle. You must use a different, unique password for every single online account. The reason is simple: data breaches are inevitable. Billions of credentials are leaked every year from breaches at major companies. If you use the same password for your LinkedIn account and your Gmail account, and LinkedIn gets hacked, attackers will immediately take that leaked email/password combination and try it on Gmail, your bank, Amazon, and everywhere else. This is called credential stuffing, and it is one of the most successful hacking techniques today. Remembering a unique, long, and complex password for every site is humanly impossible. This is where technology comes in to help. The only practical way to achieve true uniqueness across all your accounts is by using a password manager, which we will discuss in detail later. It generates and securely stores these passwords for you, so you only have to remember one very strong master
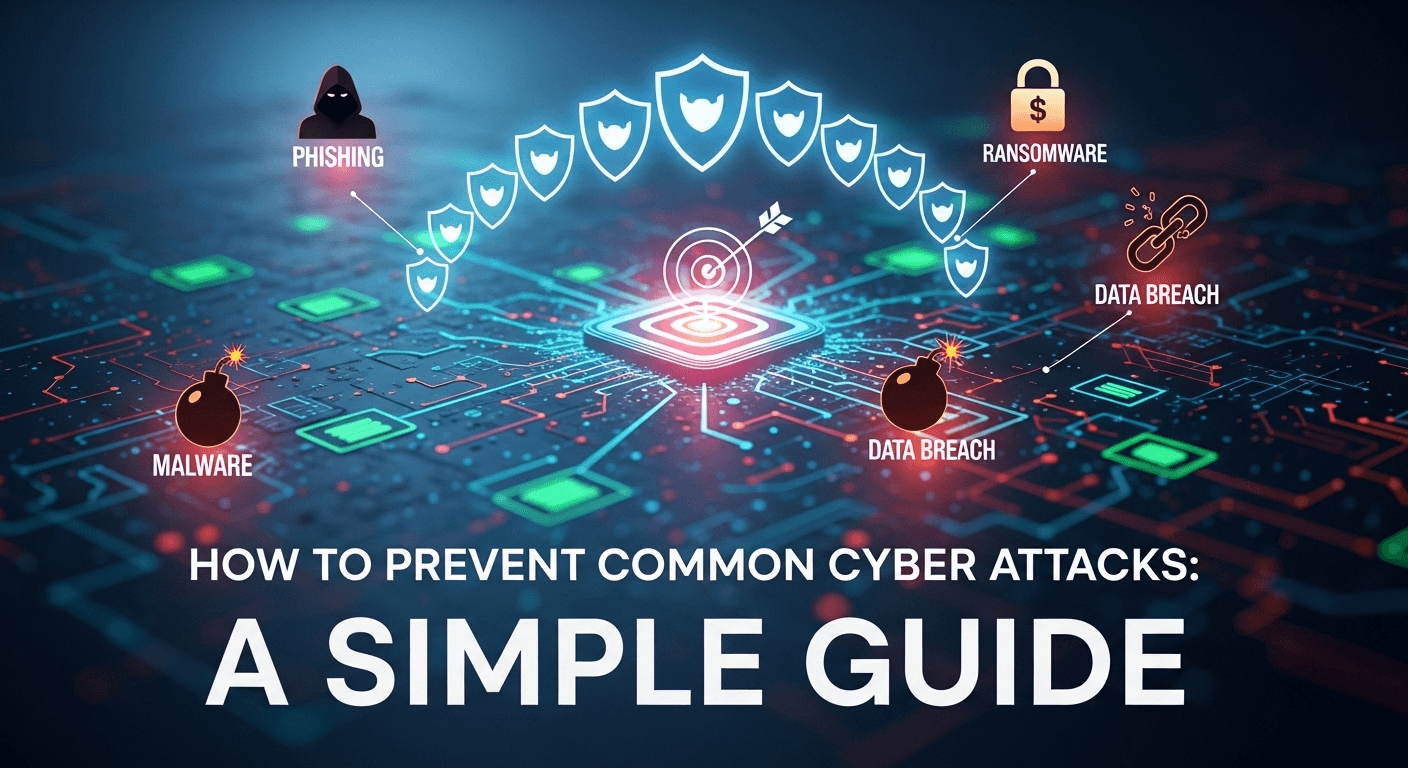
How to Prevent Common Cyber Attacks: A Simple Guide
How to Prevent Common Cyber Attacks: A Simple Guide Cyber attacks are becoming more frequent and sophisticated, but many successful breaches still exploit basic weaknesses. If you want to learn how to prevent common cyber attacks, start with strong fundamentals: understand threats, secure devices and networks, protect identities and data, prepare to respond, and build a security-first culture. This guide lays out practical, long-term strategies that anyone—from individuals to small businesses—can implement to reduce risk and recover faster when incidents occur. Understanding the landscape and applying layered defenses are essential. Below you’ll find clear steps, real-world best practices, and an easy-reference table to compare threats and countermeasures. Follow these recommendations to raise your security baseline and make it far more difficult for attackers to succeed. Understand Common Cyber Threats Knowing the enemy is the first step in how to prevent common cyber attacks. Attackers use a range of techniques—phishing, malware, ransomware, credential theft, and denial-of-service—to reach their goals. Many successful breaches begin with a simple social-engineering trick, so technical controls must be paired with user awareness. A practical approach is to categorize threats by vector (email, web, network, physical), motive (financial, espionage, disruption), and likely targets (individuals, SMBs, enterprises). By mapping your organization’s assets against that threat profile, you can prioritize defenses where they reduce the most risk. Prioritization saves time and budget and ensures high-impact assets get layered protection first. Finally, keep threat intelligence current. Subscribe to reputable feeds, review vendor advisories, and learn from public breaches. Understanding who might target you and why helps tailor controls and incident responses to realistic scenarios rather than hypothetical extremes. Phishing and Social Engineering Phishing remains the top initial access vector for many breaches. Attackers craft convincing emails, messages, or phone calls to trick users into revealing credentials, clicking malicious links, or approving fraudulent transactions. Modern phishing often uses impersonation of trusted services and urgency to bypass rational checks. To combat this, implement both technical and human controls. Technical measures include email filtering, DMARC/DKIM/SPF for authentication, and safe-link rewriting for URL scanning. Human measures include regular phishing simulations and training that focus on recognizing contextual clues—unexpected requests for credentials, mismatched domains, and unusual grammar or tone. People are a security control; empower them. Malware and Ransomware Malware (including ransomware) is delivered via email attachments, drive-by downloads, infected installers, or compromised remote access tools. Ransomware often gains a foothold through a single compromised account or an unpatched remote service and then escalates privileges and spreads laterally. Defenses include modern endpoint protection (EPP/EDR), application allow-lists, timely patching, and restricting administrative rights. Equally important are backups and tested recovery processes. Backups that are not tested or are continuously accessible to the attacker are useless, so isolate and validate backups regularly. Secure Networks and Endpoints Securing the network is not a one-off configuration; it’s a continuous discipline. Use segmentation, strong perimeter controls, and modern detection systems to limit attacker movement and speed detection. Cloud and hybrid environments require consistent policy enforcement across on-premises and cloud resources. Start by creating network zones that isolate critical assets. Put user devices on separate VLANs from servers and management interfaces. Use next-generation firewalls, intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS), and limit inbound remote access with VPNs or secure gateways. Assume the internal network will be probed—reduce the number of accessible services. Finally, keep endpoint protection up to date. Modern EDR solutions not only block known malware but also detect suspicious behavior patterns. Combine behavioral detection with threat hunting to find hidden intrusions early. Firewalls, Segmentation, and VPNs Firewalls should enforce least-privilege network flows rather than open wide permissive rules. Network segmentation reduces blast radius: if one device is compromised, the attacker cannot easily access unrelated systems. Microsegmentation in cloud environments provides more granular control for critical workloads. VPNs are useful but can be a single point of failure if misconfigured or if credentials are weak. Consider replacing or augmenting VPNs with Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) solutions that grant access based on identity, device posture, and context. Segment and verify on every connection. Endpoint Protection and Patch Management Endpoint defenses require continuous maintenance: patching operating systems, browsers, and third-party apps, and deploying agents that can detect malicious activities. Implement centralized patch management and prioritize critical updates that mitigate high-risk vulnerabilities. Also deploy application control and principle-of-least-privilege for applications. Restrict admin privileges and use endpoint encryption for data-at-rest. Combine these with logging and centralized telemetry to quickly investigate suspicious events. Protect Identities and Access Compromised credentials are a leading cause of breaches. Strong identity security reduces both the likelihood and impact of attacks. Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA), strong password policies, and account lifecycle management to secure identities from creation to deprovisioning. Beyond MFA, adopt a least-privilege access model. Regularly review permissions, automate access approvals, and revoke rights when roles change. Use single sign-on (SSO) judiciously and monitor SSO activity for anomalies. Finally, treat service accounts like human accounts: give them the minimal privileges, rotate keys, and monitor their usage. Identity is the new perimeter—protect it accordingly. Multi-factor Authentication (MFA) MFA adds a second verification layer—something you have (token), something you know (PIN), or something you are (biometrics). It significantly reduces the risk of account takeover even if passwords are leaked. Use phishing-resistant MFA (hardware tokens, FIDO2/WebAuthn) for high-privilege accounts. Enforce MFA across all remote access and privileged operations. Ensure backup MFA methods are secure, and educate users about MFA fatigue or social engineering that attempts to bypass MFA. Least Privilege and Access Reviews Least privilege limits what accounts can do and access. Implement role-based access control (RBAC), periodic access reviews, and time-limited elevated access (just-in-time, JIT). Automate onboarding and offboarding to avoid orphaned accounts. Conduct quarterly or monthly audits of privileged accounts and require justification for continued access. Revoking unnecessary access is one of the most effective risk reducers. Application and Data Security Applications are a frequent attack target—vulnerabilities in web apps or APIs can provide remote code execution or data exposure. Secure development practices prevent vulnerabilities before deployment and reduce remediation
How to Secure Windows from Intruders: A Full Guide
In today's digitally interconnected world, your Windows computer is more than just a device; it's a gateway to your personal and professional life. It holds sensitive documents, precious memories, and financial information. This makes it a prime target for intruders, from opportunistic hackers to sophisticated cybercriminals. Understanding how to secure Windows from intruders is no longer an optional skill for the tech-savvy—it's an essential practice for every user. This guide will walk you through a multi-layered defense strategy, transforming your PC from a potential target into a digital fortress. We will cover everything from foundational user account security to advanced system hardening, ensuring you have the knowledge to protect what matters most. Foundational Security: User Accounts and Passwords The first line of defense against any unauthorized access is centered around who is allowed to use the computer and what they are permitted to do. User accounts and their corresponding passwords are the gatekeepers of your digital kingdom. A weak or compromised password is like leaving your front door unlocked. Intruders often use automated tools that can guess millions of password combinations in seconds, making simple or common passwords incredibly vulnerable. Therefore, establishing a robust account and password policy is the non-negotiable cornerstone of your entire security posture. Strengthening this foundational layer involves more than just picking a "strong" password. It requires a strategic approach to account management, embracing principles used by security professionals worldwide. This includes understanding the difference between user types, limiting privileges to prevent system-wide damage, and adding layers of verification that go beyond a simple password. By focusing on these core elements first, you significantly raise the bar for any would-be intruder, forcing them to overcome multiple hurdles before they can even begin to access your system. Use Strong, Unique Passwords and a Password Manager A strong password is your primary shield. Modern security standards dictate that a strong password should be long (at least 12-15 characters), complex (a mix of uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols), and unpredictable (avoiding common words, names, or keyboard patterns like "qwerty"). Your dog's name followed by "123" is not secure. A better approach is to use a passphrase, such as "Correct!Horse-Battery_Staple7," which is both memorable and exceptionally difficult for machines to guess. Crucially, you must use a unique password for every single account. If you reuse passwords and one service is breached, intruders will use those credentials to try to access everything else, including your Windows account. Remembering dozens of unique, complex passwords is an impossible task for any human. This is where a password manager becomes an indispensable tool. Reputable password managers like Bitwarden, 1Password, or LastPass generate, store, and auto-fill highly secure passwords for all your accounts. You only need to remember one strong master password to unlock your vault. This not only bolsters your security exponentially but also improves convenience. Using a password manager is one of the single most impactful security changes you can make. Implement the Principle of Least Privilege (POLP) The Principle of Least Privilege is a fundamental cybersecurity concept that states a user should only have the access levels essential to perform their job or daily functions. In Windows, this means you should not use an Administrator account for your day-to-day activities like browsing the web, checking email, or word processing. An Administrator account has full control over the system; if it's compromised while you're browsing, the malware or intruder also gains full control. They can install malicious software, delete critical files, and lock you out of your own computer. Instead, create a Standard User account for your daily use. A Standard User account cannot install most software or make system-level changes without providing an administrator password. This creates a critical security barrier. When a piece of malware tries to execute, a User Account Control (UAC) prompt will appear, asking for the administrator password. If you weren't intentionally trying to install something, this prompt is a massive red flag, giving you a chance to deny the request and prevent an infection. Operating as a Standard User contains the potential damage from a simple click on a malicious link. Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a security layer that requires more than just a username and password to log in. It adds a second (or third) "factor" of verification to prove your identity. Even if an intruder steals your password, MFA will block them because they won't have access to your second factor. This is an incredibly effective way to secure your Microsoft Account, which is often linked to your Windows login. The most common factors are: Something you know: Your password. Something you have: Your phone (receiving a code via SMS or an authenticator app) or a physical security key. Something you are: Your fingerprint or face (biometrics, viaWindows Hello*). For your Microsoft Account, you can easily set up MFA to use the Microsoft Authenticator app. When you log in from a new device, you'll receive a notification on your phone asking you to approve the login. This simple step makes a brute-force password attack nearly useless against your account and is one of the best defenses against phishing attacks that successfully steal your credentials. Leveraging Built-in Windows Security Tools Many users are unaware that modern versions of Windows (10 and 11) come equipped with a powerful and integrated suite of security tools. Gone are the days when a third-party antivirus and firewall were absolute necessities. Microsoft has invested heavily in creating a robust, built-in security platform that is more than capable of protecting the average user, provided it is configured correctly. These tools are designed to work seamlessly with the operating system, offering a level of integration that third-party software often can't match. Relying on these native tools simplifies your security setup, reduces potential system performance impacts, and eliminates conflicts that can arise from running multiple security programs. The key is to know what these tools are, how they work, and how to ensure they are enabled and
Essential Ways to Protect Your Personal Data Online
In our hyper-connected world, personal data has become the new currency. Every click, every search, and every social media post contributes to a vast digital profile that companies and, unfortunately, malicious actors find incredibly valuable. The casual way we share information can leave us vulnerable to everything from targeted advertising to sophisticated identity theft. Because of this, understanding the essential ways to protect your personal data online is no longer optional—it's a critical life skill. This guide will walk you through comprehensive strategies and actionable steps to reclaim control over your digital identity and fortify your online presence against prying eyes. Understanding Your Digital Footprint: The First Step to Protection Before you can effectively protect your data, you must first understand what you are protecting. Your digital footprint is the trail of data you leave behind when you use the internet. It includes everything from the websites you visit, the emails you send, and the information you submit to online services. This footprint is composed of two main types: active and passive. Your active digital footprint includes data you adeliberately share, such as posting on social media, filling out online forms, or sending an email. Your passive digital footprint, on the other hand, is data collected without you actively providing it, like your IP address, browsing history tracked via cookies, and location data gathered by apps. Recognizing the extent of your digital footprint is a sobering but necessary exercise. Think about the accounts you've created over the years—old email addresses, forgotten social media profiles, forum memberships, and subscriptions to services you no longer use. Each of these represents a potential vulnerability. A data breach at a company you haven't interacted with in a decade can still expose your email and password, which you might have reused elsewhere. This is why a proactive approach is crucial; you cannot secure what you do not know exists. Taking stock of this footprint is the foundational step in building a robust online security posture. It allows you to identify and eliminate old, unnecessary accounts that serve only as liabilities. By understanding how and where your data is stored, you can begin to make more informed decisions about what information you share and with whom. This initial audit transforms the abstract concept of "online data" into a tangible inventory of your personal information scattered across the web, empowering you to start the cleanup process and implement stronger protections moving forward. ### How to Audit Your Online Presence Auditing your online presence is like doing a deep clean of your digital life. The first and most straightforward step is to search for yourself online. Use major search engines like Google, Bing, and DuckDuckGo. Search for your full name, your name with your city, your email addresses, and any old usernames you can remember. Enclose your name in quotation marks (e.g., "John Doe") to get more precise results. This will show you what information is publicly accessible, from social media profiles and public records to old news articles or forum posts you may have forgotten about. Once you have a list of accounts and mentions, the real work begins. Visit each service and profile you find. If it's an account you no longer need, find the option to permanently delete it, not just deactivate it. Deactivation often leaves your data on the company's servers. For accounts you wish to keep, dive deep into the privacy and security settings. This is a critical step. Review who can see your posts, who can find you via your email or phone number, and what data the platform is collecting. Services like Google's Privacy Checkup and Facebook's Privacy Settings are powerful tools that guide you through this process, allowing you to limit data tracking and public visibility. Fortifying Your Accounts: The Core of Digital Defense The most direct line of defense for your personal data is the security of your individual online accounts. Each account, whether for banking, email, or social media, is a gateway to a piece of your life. If a cybercriminal gains access to just one critical account—like your primary email—they can often initiate a domino effect, using it to reset passwords for your other services and take over your entire digital identity. Therefore, making your accounts as difficult as possible to breach is a non-negotiable aspect of online safety. This fortification process goes beyond simply using a "strong" password. It involves a multi-layered approach to security. You must treat your login credentials as the keys to your digital kingdom because that is precisely what they are. This means adopting habits and using tools that were once considered overkill but are now standard practice for anyone serious about their security. From creating truly random passwords to enabling an extra layer of verification, these methods work together to create a formidable barrier. The goal is to make the effort required to compromise your account greater than the potential reward for the attacker. Most cybercriminals are opportunistic; they look for easy targets. By implementing robust security measures, you make yourself a much harder target, encouraging them to move on to someone with weaker defenses. This proactive stance ensures that even if a service you use suffers a data breach, your account is less likely to be compromised. ### The Art of Crafting Unbreakable Passwords The advice to "use a strong password" is common, but what does it actually mean? A truly strong password is not just a word with a few numbers and symbols tacked on (e.g., `Password!1`). Modern password-cracking software can guess such combinations in seconds. Instead, the focus should be on length and randomness. A better approach is to use a passphrase—a sequence of random words strung together, like `correct-horse-battery-staple`. This is significantly longer, easier for you to remember, and exponentially harder for a computer to brute-force. The best practice is to use a unique and random password for every single online account. Reusing passwords is one of the most dangerous habits in the digital world. If
What Happened to Mark Sanchez? His Life After the NFL
Of course. As an SEO expert, I will craft a unique, engaging, and SEO-optimized article that meets all your requirements, including the strict relevance rules. Here is the article: In the fast-paced world of professional sports, narratives can shift in an instant. While fans today might be captivated by the tactical chess match of a Chelsea vs Liverpool fixture or debating the dominant careers of defensive stalwarts like Arthur Jones, there are names from the recent past that still echo with a mix of triumph, what-ifs, and genuine curiosity. One such name is Mark Sanchez. The former USC standout and New York Jets quarterback was once hailed as the savior of a franchise, a charismatic leader destined for greatness. Then, his career took a different, more complicated path. So, what happened to Mark Sanchez? His story didn't end on the football field; it simply entered a new chapter, one defined by resilience, reinvention, and finding a new voice. The Rise of the 'Sanchize': A Look Back at His NFL Career Before he became a well-known television analyst, Mark Sanchez was "The Sanchize," a top-five draft pick who carried the immense pressure of being the face of the New York Jets. His journey began with spectacular promise at the University of Southern California (USC), where he led the Trojans to a Rose Bowl victory and a near-perfect season. His combination of arm talent, swagger, and movie-star good looks made him the perfect candidate for the bright lights of New York City when the Jets famously traded up to select him with the fifth overall pick in the 2009 NFL Draft. The investment paid off immediately. In his first two seasons, Sanchez did something legendary Jets quarterback Joe Namath never did: he led the team to back-to-back AFC Championship games on the road. He became the first rookie quarterback to win his first two playoff games and only the second in NFL history to win a playoff game on the road. He was calm under pressure, made crucial throws, and seemed poised to be the franchise quarterback the Jets had been seeking for decades. The team was built around a dominant defense and a powerful running game, and Sanchez was the composed field general tasked with steering the ship. For a fleeting moment, he was on top of the football world. However, the immense pressure of the New York media market and the league's constant evolution began to take their toll. While his early playoff success was undeniable, his regular-season performances were often inconsistent. Turnovers became a recurring issue, and the narrative surrounding him began to shift from savior to liability. This culminated in one of the most infamous plays in NFL history: the "Butt Fumble" on Thanksgiving Day 2012. That single, comical, and unfortunate play became a symbol of the Jets' struggles and unfairly began to define Sanchez's career, overshadowing the significant successes he had achieved just a couple of years prior. The Highs – Reaching the Pinnacle of the AFC Mark Sanchez's early career was a whirlwind of success. After a stellar, albeit short, career as a starter at USC, he entered the NFL with immense hype. The Jets, under head coach Rex Ryan, saw him as the final piece of a championship puzzle. Ryan’s brash confidence and the team's "Ground and Pound" philosophy provided the perfect environment for a young quarterback. Sanchez wasn't asked to win games by himself; he was asked to manage them, avoid critical mistakes, and make timely throws, which he did masterfully during those two playoff runs. His victories against the favored Indianapolis Colts, New England Patriots, and San Diego Chargers in the postseason were not flukes. They were the product of a quarterback who, despite his youth, showed remarkable poise in the biggest moments. He out-dueled Peyton Manning and Tom Brady in consecutive road playoff games, a feat few quarterbacks can claim. These moments were the peak of "The Sanchize" era, where he looked every bit the part of a top-tier NFL quarterback leading a legitimate Super Bowl contender. This period cemented his status as a winner in the eyes of the Jets faithful. The Lows and The New York Spotlight Unfortunately, sustained success in the NFL is incredibly difficult, especially under the relentless scrutiny of the New York media. As the team's offensive supporting cast began to decline, more pressure fell on Sanchez's shoulders. His decision-making became more erratic, and the interceptions mounted. The confidence that defined his early years seemed to wane with every critical headline and talk-radio debate. The team's identity, once so clear, became muddled, and Sanchez became the primary scapegoat. The "Butt Fumble" against the New England Patriots was the nadir. While a single play should never define a career, its bizarre nature made it an instant, viral meme that has persisted for over a decade. It was the public face of a team's collapse and, for Sanchez, a moment he couldn't escape. This play, combined with mounting losses and a shoulder injury that cost him the entire 2013 season, ultimately signaled the end of his time in New York. His journey with the Jets was a microcosm of an NFL career: glorious highs and crushing lows, all played out on the biggest stage. The Journeyman Years: Life After the Jets After parting ways with the Jets, Mark Sanchez embarked on the second phase of his NFL career: the life of a journeyman. This is a common path for former starting quarterbacks, where they leverage their experience and knowledge to serve as high-quality backups and mentors for younger players. His first stop was with the rival Philadelphia Eagles under coach Chip Kelly. In 2014, he stepped in for an injured Nick Foles and played surprisingly well, setting career highs in completion percentage and passer rating while leading the team to a 4-4 record in his starts. This period proved he could still be an effective quarterback in the right system. Following his stint in Philadelphia, Sanchez's tour continued.